Chris Tasker, CEO of Global Cannabinoid Solutions (GCS), recently published a video titled, “Understanding the Endocannabinoid System (ECS): Clinical Foundations & Pharmacological Insights”.
We found the video provided much needed clarity and context around the endocannabinoid system that we decided to reach out to Chris himself for his blessing to share it on our blog.
(Thanks so much, Chris, for your time in putting this together!)
You can watch the full video below, or skim through the quick summary that follows.
Note: the written summary only covers the key takeaways – we greatly encourage you to watch the full video for deeper insights! 👇
EXECUTIVE SUMMARY
The endocannabinoid system (ECS) is one of the most fascinating and underappreciated biological systems in the human body. It’s a master regulator, working tirelessly to maintain balance across multiple physiological systems. From mood and memory to inflammation and metabolism, the ECS plays a pivotal role in keeping us healthy. For those working in the cannabis industry, understanding the ECS is not just a scientific curiosity – it’s the foundation for unlocking the therapeutic potential of cannabinoids.
Table of Contents
1. Introduction: Why the ECS Matters
2. How was the Endocannabinoid System discovered?
3. What Is the ECS? Components and Functions
4. How the ECS Maintains Balance (Homeostasis)
5. Endocannabinoids: Anandamide vs. 2-AG
6. Stress, ECS, and Adaptation
7. The ECS Beyond the Brain: Gut, Skin, and More
8. Therapeutic Potential: Targeting the ECS
Introduction: Why the ECS Matters
Let’s start with the big picture.
The endocannabinoid system isn’t just a niche topic for cannabis enthusiasts or researchers. It’s a biological system that’s central to human health. As Chris, founder and CEO of Global Cannabinoid Solutions, puts it:

For those in the cannabis industry, understanding the ECS is crucial. It’s the key to explaining how cannabinoids like THC and CBD interact with the body, and it’s the foundation for developing effective cannabis-based therapies.
How was the Endocannabinoid System discovered?
The ECS was discovered through research into Delta-9-tetrahydrocannabinol (THC), the psychoactive compound in cannabis.
Scientists wanted to know: How does THC actually work in the body?
This question led to one of the most important discoveries in neuropharmacology. In 1992, Raphael Mechoulam and his colleagues isolated anandamide, the first identified endocannabinoid. Shortly after, they discovered 2-arachidonylglycerol (2-AG). These findings revealed that humans (and other animals) have an endogenous cannabinoid signalling system.

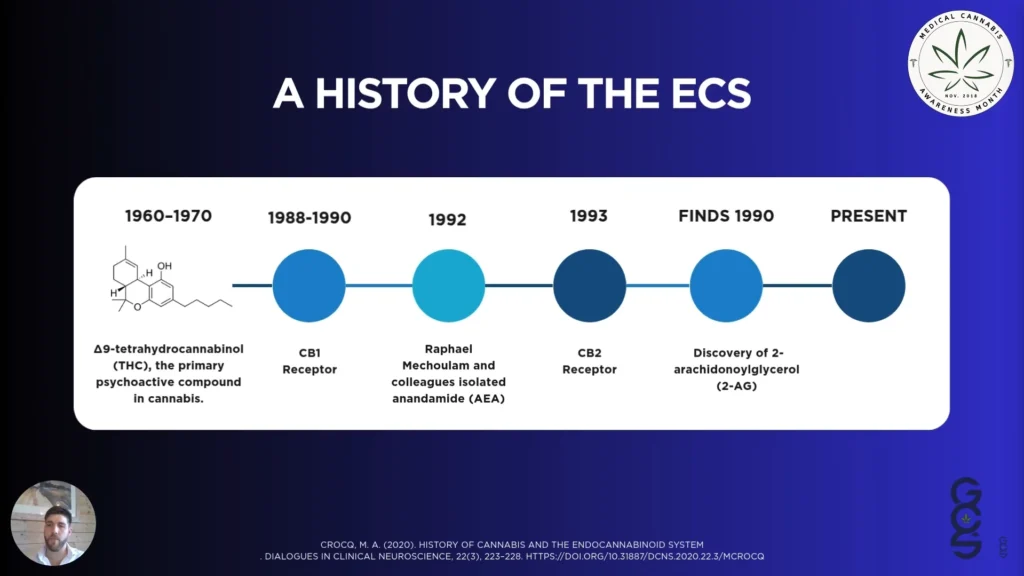
This was a game-changer. What started with a plant compound ended up revealing a powerful system that our bodies rely on to maintain balance.
What Is the ECS? Components and Functions
At its core, the ECS is a biological system composed of three key components:
- Endocannabinoids: Molecules like anandamide and 2-AG, produced naturally by the body.
- Receptors: CB1 and CB2 receptors, which endocannabinoids bind to.
- Enzymes: Proteins that synthesise and degrade endocannabinoids.
These components work together to regulate physiological balance across multiple systems, including the nervous, immune, and digestive systems.

How the ECS Maintains Balance (Homeostasis)
The ECS is all about balance. It responds dynamically to changes in the body, working to maintain stability despite external or internal stresses.
For example, the ECS modulates neurotransmission by controlling the release of neurotransmitters. This helps regulate mood, memory, and pain perception. It also plays a key role in inflammatory regulation, energy metabolism, and even reproductive processes.


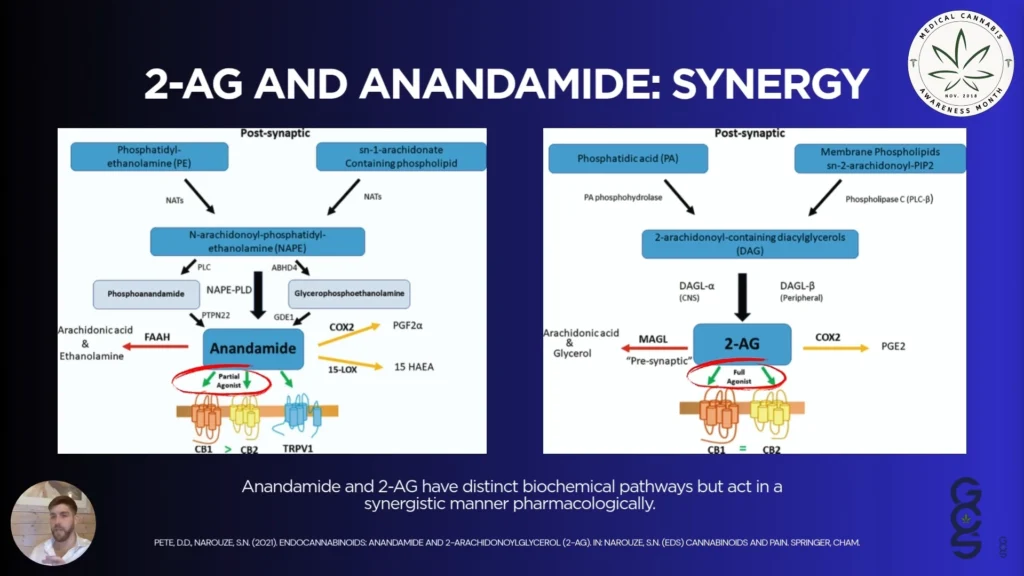
Endocannabinoids: Anandamide vs. 2-AG
Anandamide and 2-AG are the two main endocannabinoids in the ECS, but they have distinct roles.
- Anandamide: Often involved in fine-tuning synaptic activity, mood modulation, and subtle shifts in behaviour.
- 2-AG: Typically present in higher concentrations and involved in broad, rapid neuromodulation, especially during acute stress or injury.
Emerging research suggests that these molecules work together in a layered signalling mechanism. 2-AG delivers the initial push, while anandamide modulates the aftermath.
Stress, ECS, and Adaptation
Stress has a profound impact on the ECS.
When the brain experiences acute stress, anandamide levels drop in the amygdala, allowing the stress response to kick in. Later, 2-AG levels rise to help shut down the stress response and promote recovery.
This adaptive mechanism highlights the ECS’s role in managing stress and maintaining balance.

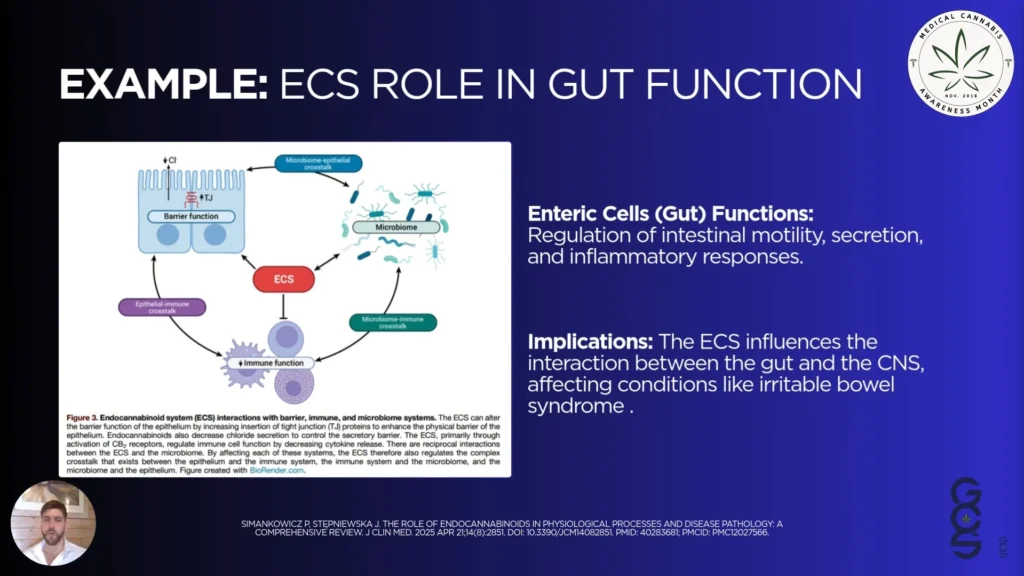
The ECS Beyond the Brain: Gut, Skin, and More
The ECS isn’t just a brain-based system. It’s active in the gut, skin, and other tissues, playing a role in everything from intestinal homeostasis to skin barrier function.
In the gut, for example, the ECS strengthens the physical barriers in the intestinal epithelium, regulates fluid balance, and suppresses inflammation. It also interacts with the gut microbiota, creating a bidirectional relationship that influences overall health.
Therapeutic Potential: Targeting the ECS
The ECS is a promising therapeutic target for a wide range of conditions, including chronic pain, anxiety, autoimmune disorders, and neurodegenerative diseases.
By modulating ECS activity, cannabis-based therapies can help restore balance and improve quality of life for patients.
For example, PEA (palmitoylethanolamide), an endocannabinoid-like molecule, has been used to reduce neuroinflammation and improve mitochondrial function in autistic individuals.

Final Thoughts
The endocannabinoid system is a marvel of human biology.
It’s dynamic, adaptive, and deeply involved in maintaining health and balance. For those in the cannabis industry, understanding the ECS isn’t just a scientific curiosity – it’s a professional necessity.
As research continues to uncover the complexities of this system, the opportunities for innovation in cannabis-based therapies are endless. So whether you’re growing plants, developing products, or educating patients, remember: the ECS is at the heart of it all.
About Chris Tasker

Christopher Tasker bridges cannabinoid science and business, leveraging research expertise (including an MRes in Cannabinoid Science and studies on cancer and IBD) to lead Global Cannabinoid Solutions (GCS), where he turns cutting-edge cannabis research into actionable industry strategies.
🌐 Follow GCS & Stay Connected:
🧠 Join the GCS Community – for free access to the GCS global network, insights, and industry updates.